Chronic Appendicitis | Symptoms | Causes
Chronic appendicitis is a rare medical condition. It can be difficult to diagnose because the symptoms may come and go, and they can also be mild. The most common symptom is abdominal pain. The likely cause is inflammation or an obstruction in your appendix.
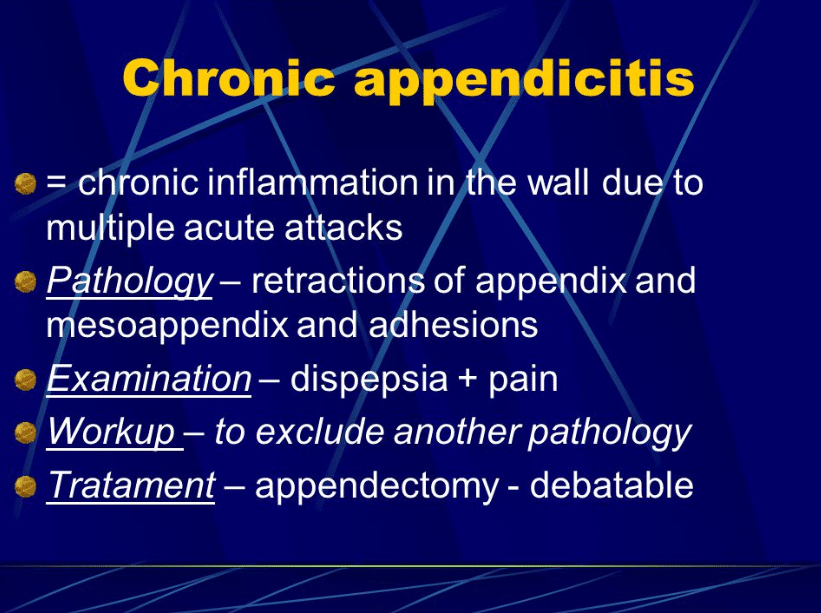
It’s important to get the correct diagnosis because chronic appendicitis can be life-threatening in some cases. People with chronic appendicitis have appendicitis that lasts for long periods of time. This means appendicitis that is present for longer than a week.
Chronic Appendicitis Symptoms
The symptoms of chronic appendicitis may be mild. In some cases, abdominal pain is the only symptom with chronic appendicitis. The pain is usually in the lower right side of the abdomen. It may also appear near the belly button and move to the lower right side of the stomach in some cases. The pain can vary from sharp to dull, but it’s more common for it to be dull.
Other symptoms of chronic appendicitis include:
- abdominal pain
- fever
- abdominal swelling and tenderness
- fatigue or lethargy, which is a lack of energy
- malaise, which is a general feeling of discomfort or illness
Some people might also experience nausea or diarrhea. Symptoms may come and go, which can make the condition more difficult to diagnose.
If you have any of these symptoms and they continue to become more severe, consider going to the doctor. They may be a sign of a serious medical problem.
Chronic appendicitis vs. acute appendicitis
Chronic appendicitis and acute appendicitis are sometimes confused. In some cases, chronic appendicitis isn’t diagnosed until it becomes acute appendicitis.
Chronic appendicitis can have milder symptoms that last for a long time, and that disappear and reappear. It can go undiagnosed for several weeks, months, or years.
Acute appendicitis has more severe symptoms that appear suddenly within 24 to 48 hours of trusted Source. Acute appendicitis requires immediate treatment.
Other symptoms of acute appendicitis include:
- nausea with or without vomiting
- low-grade fever
- constipation or diarrhea
- lack of appetite
- inability to pass gas
Appendicitis usually occurs when an obstruction, such as a foreign object or calcified stool, blocks the inner cavity or appendiceal lumen of the appendix.
appendicitis may occur when the appendiceal lumen is only partially blocked. However, the blockage is likely to worsen over time by causing pressure to build.
When this happens in people with appendicitis, the pressure may overcome the partial obstruction, and the symptoms will reduce in intensity or go away altogether.
The symptoms will then return the next time the blockage causes the appendix to become inflamed.
Chronic appendicitis Causes
Chronic appendicitis may occur for many different reasons and many cases do not have a clear cause.
Often, appendicitis occurs due to inflammation and obstruction of the appendix. Other possible causes include:
- accumulation of fecal matter, which can happen if someone is constipated
- calcified fecal deposits, also known as ‘appendix stones’
- trauma to the abdomen
- tumors
- enlarged lymph nodes and glands
- worms
- a buildup of foreign objects, such as stones, marbles, or pins
Diagnosis and treatment
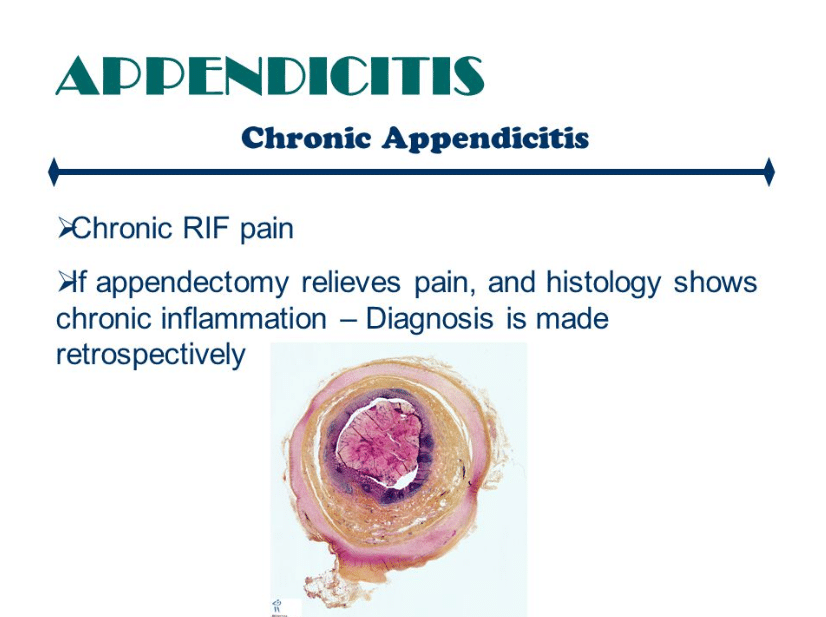
A doctor will initially do a physical exam to determine whether the abdomen is tender and where the pain is located. They will also ask questions about the symptoms and a person’s medical history.
In most cases, a doctor will do several tests to rule out other medical conditions that have the same symptoms.
The conditions the doctor may attempt to rule out include:
- urinary tract infection
- kidney infection
- Crohn’s disease
- ulcerative colitis
- ovarian cysts
- pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- other gastrointestinal disorders
The tests used to rule out these conditions include:
- blood tests
- a pelvic exam
- a pregnancy test
- urinalysis or testing a person’s urine
- computerized tomography (CT) scan
- abdominal ultrasound
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
If appendicitis is diagnosed, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics or may advise draining the pus that has formed around the appendix due to the infection.
The most common treatment, however, is to have the appendix removed altogether. This surgery is called an appendectomy.
An appendectomy is usually performed using laparoscopic surgery, which is minimally invasive. It is also known as keyhole surgery and is performed under general anesthetic.